Andrew Laker/AP
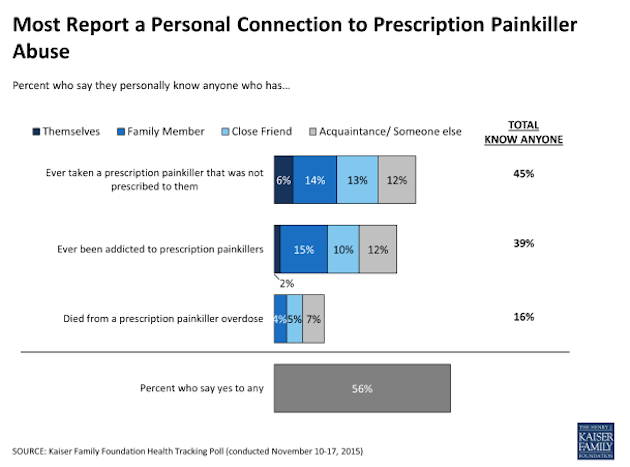
A troubling poll published Tuesday shows the extent of America’s addiction to prescription painkillers. More than half of Americans now report a personal connection to painkiller abuse, 16 percent know someone who has died from an overdose, and 9 percent have seen a family member or close friend die.
“It shows that the issue affects a large share [of people], over half the population,” says Bianca DiJulio, associate director for public opinion and survey research at the Kaiser Family Foundation, which conducted the survey. “And half say that it should be a top priority for their lawmakers.”
Researchers spoke by phone this month with more than 1,300 people aged 18 years and older across the United States, who were selected to match the demographic makeup of the country. White Americans were the most likely to report personal experience with the abuse of prescription painkillers, which include opioids such as Vicodin and OxyContin and benzodiazepines such as Xanax. Sixty-three percent of white respondents, 44 percent of black respondents, and 37 percent of Hispanics said they had either personally abused painkillers or knew someone who had taken painkillers without a prescription, been addicted to painkillers, or died of an overdose.
Overall, 56 percent of respondents reported a personal connection to painkiller abuse, with young and middle-aged Americans more likely to report familiarity with painkiller abuse than Americans aged 65 and older.
The United States is caught in “a prescription painkiller overdose epidemic,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Nearly 2 million Americans abused prescription painkillers in 2013, with 44 people dying from an overdose each day.
Drug overdoses, including deaths from prescription drug use, were the leading cause of accidental death in the United States in 2013. Among the respondents, “half thought the leading cause of accidental deaths was car accidents,” DiJulio says.
The issue, along with rampant heroin addiction, has reached such proportions that President Barack Obama last month announced steps to increase training for doctors who prescribe painkillers and expand access to treatment for drug addicts.
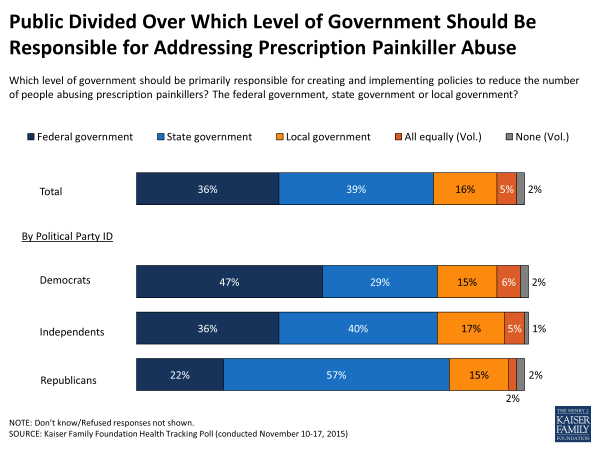
But Kaiser’s survey shows that, even as many Americans agree the government should act, there is no agreement as to how. Republicans in the survey were significantly more likely to say state governments should be in charge of responding to the epidemic, while Democrats saw this as the responsibility of the federal government.