<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com">smereka</a>/Shutterstock ; <a href="http://www.shutterstock.com">dedMazay </a>/Shutterstock
You vaguely know how DNA works, right? You get it from your parents. Well, hold onto your britches, because scientists from down under are about to turn your world upside down.
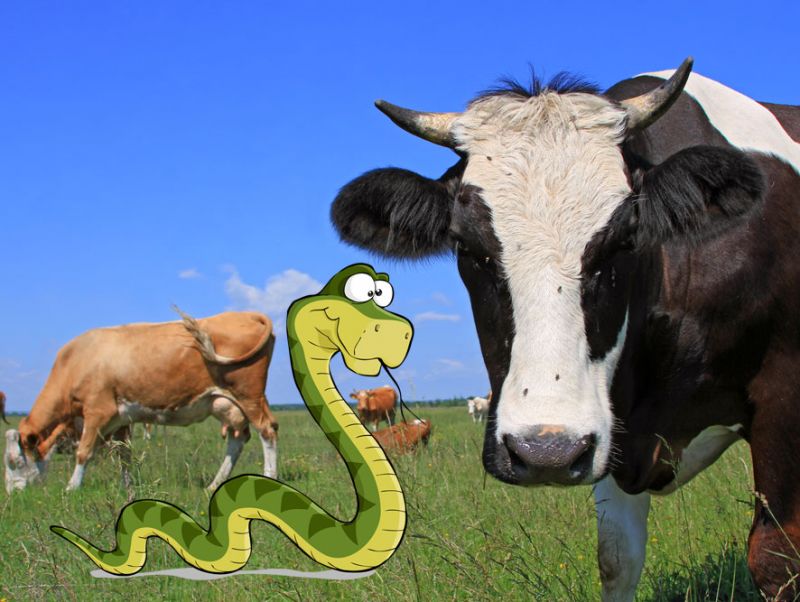
A study by Australia’s Adelaide and Flinders Universities and the South Australian Museum has found that in complex organisms, DNA is not only transferred from a parent to its offspring like your science book told you, but can also be “laterally” transferred between species. The research, published in the peer-reviewed Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in the US, involved comparing dozens of DNA sequences from different species. It found that cows inherited up to a quarter their genes from reptiles.
“[I]n higher organisms, vertebrates, mammals and so on we tend to believe that later or horizontal transfer of genetic material just doesn’t really happen,” Prof. David Adelson, study lead and head of Molecular and Biomedical Science at the University of Adeliade told Australian ABC News. “But what we’ve shown is that there are DNA segments…called jumping genes…which are able to jump between species.”
The similar DNA sequence that the two species share is able to “cut and paste itself within the genome,” and thus replicate itself and jump to another species, Adelson explains. In that way, it’s similar to how a retrovirus like HIV works, except it has “no way of making an infectious particle, so it’s a bit of a mystery how it gets from [one] species to another,” Adelson concedes.
He speculates that the DNA sequence could have “hitchhike[ed] as part of another virus,” or could have been carried from snakes to cows by ticks, but that remains to be seen, as does how much mixing and matching there is among other species. “There’s potential to see there’s a lot more room for horizontal transfer than we previously supposed,” Adelson says.
His next project will involve looking at whether human DNA sequences may also have jumped from other species. Who knows, maybe we’re 32 percent shrimp.