<a href="http://www.istockphoto.com/photo/sick-woman-driver-64495947?st=b601613">kieferpx</a>/iStock
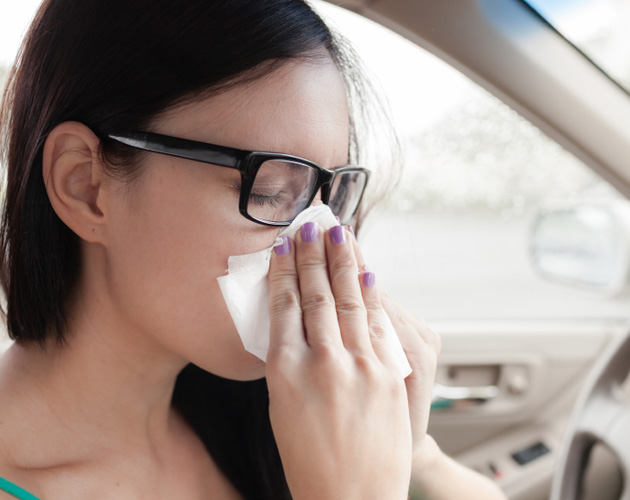
Viruses are hitching a ride with commuters on the nation’s roads and railways, adding to the chaotic movement that makes seasonal outbreaks difficult to track and contain.
In a study published Thursday in PLOS Pathogens, researchers at Emory University tracked genetic variations in two strains of influenza between 2003 and 2013. They concluded that states highly connected by ground transit tended to have similar genetic variations of the flu, and they matched their findings with illness case data that showed closely timed epidemic peaks in those states. The researchers believe ground transit connectivity may be a better indicator of where a disease is likely to spread than air travel connections or even geographic proximity, though they say both remain important factors.
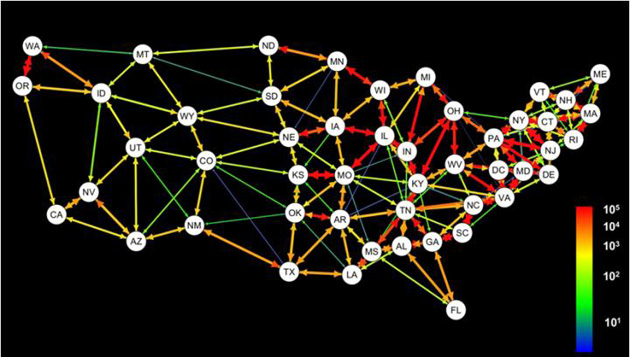
Modern transport networks complicate the movement of viruses: In the past, contagion moved person to person and village to village, resulting in “wave-like patterns” of genetic variation that correspond to geographic distance, the report says. But with 3.8 million people in the United States taking ground transportation across state borders each day and 1.6 million doing so by air, the spread of illness has become far more chaotic: Transcontinental flights help foster bicoastal outbreaks, while well-traveled commuter corridors between Kansas and Missouri may mean those states share illnesses as neighboring areas go unscathed.
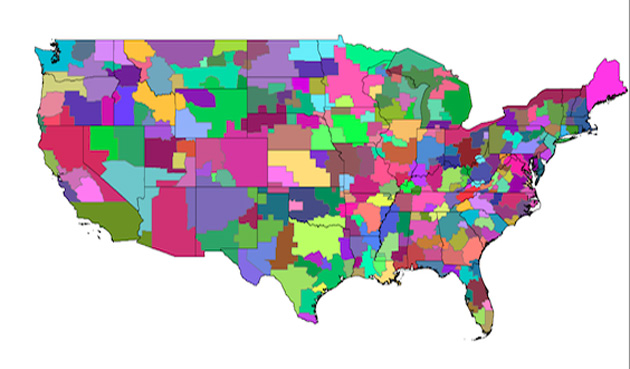
The researchers hope their study, which they believe to be the first of its kind at the scale of the continental United States, will help epidemiologists better understand influenza’s seemingly unpredictable spread.