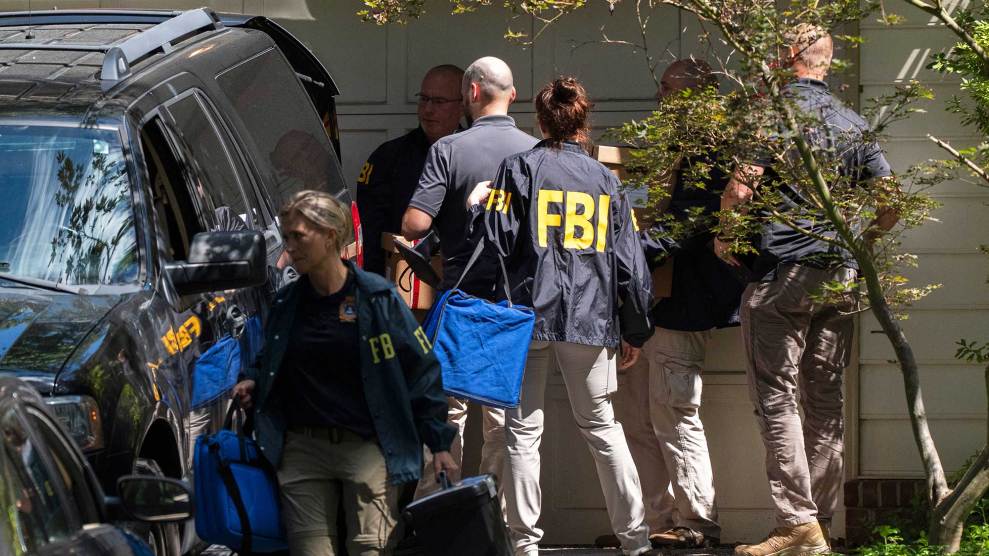
Jim Webb speaking at the "Rally for American Coal Jobs" in 2010.Pete Marovich/ZUMA
Hillary Clinton may be dominating every poll of potential Democratic hopefuls for the White House, but some progressives are desperate to find a candidate who will challenge her from the left. Groups have sprung up to encourage Elizabeth Warren to take a stab at the nomination, but with the Massachusetts senator repeatedly saying she isn’t running, liberal activists will likely have to turn elsewhere—perhaps to socialist Sen. Bernie Sanders (Vt.) or Maryland Gov. Martin O’Malley—if they aren’t satisfied with Clinton. But so far, the only Democratic alternative officially in the race is former Virginia Sen. Jim Webb, who launched an exploratory committee in November.
A former Secretary of the Navy under President Ronald Reagan, Webb is being touted by some on the left as an Appalachian populist who could champion causes Clinton would rather ignore. The Nation‘s William Greider, for example, lauded Webb’s presidential ambitions in a column headlined “Why Jim Webb Could be Hillary Clinton’s Worst Nightmare.” Greider praised Webb’s non-interventionist tendencies in foreign policy (Webb was a vocal opponent of the Iraq War). “I think of him as a vanguard politician—that rare type who is way out ahead of conventional wisdom and free to express big ideas the media herd regards as taboo,” Greider wrote, while acknowledging that Webb was unlikely to win.
There’s at least one key issue, however, on which Webb’s record is far from progressive: global warming. That’s a big deal. Unlike Obamacare and financial reform, much of the progress President Barack Obama has made on climate change rests on executive actions that his successor could undo. At first glance, Webb might look like a typical Democrat when it comes to environmental policy. The League of Conservation Voters gives him a lifetime score of 81 percent—on par with Hillary Clinton’s 82 percent rating, though far below Sanders at 95 percent. And unlike most of the Republican presidential hopefuls, he acknowledges that humans are causing climate change. He even supports solving the problem—at least in theory.
But when it came to actual legislation, Webb used his six years in the US Senate to stand in the way of Democratic efforts to combat climate change. Virginia, after all, is a coal state, and Webb regularly stood up for the coal industry, earning the ire of environmentalists. As Grist‘s Ben Adler succinctly summed it up, “Jim Webb sucks on climate change.”
Perhaps Webb’s biggest break with the standard Democratic position on climate is his vocal opposition to the use of EPA rules under the Clean Air Act to limit carbon emissions from coal power plants. Earlier this year, the Obama administration proposed regulations that could cut existing coal plant emissions by as much as 30 percent below 2005 levels by 2030. Those new rules became a key factor in the historic climate deal Obama recently reached with China, and they will almost certainly figure prominently in next year’s Paris climate negotiations. But back in 2011, Webb went to the floor of the Senate to denounce the idea that the federal government has the power to regulate carbon emissions under existing law. “I am not convinced the Clean Air Act was ever intended to regulate or classify as a dangerous pollutant something as basic and ubiquitous in our atmosphere as carbon dioxide,” he said.
Webb also supported legislation from fellow coal-state Sen. Jay Rockefeller (D-W.Va.) that would have delayed the EPA’s authority to add new rules governing coal plant emissions. “This regulatory framework is so broad and potentially far reaching that it could eventually touch nearly every facet of this nation’s economy, putting unnecessary burdens on our industries and driving many businesses overseas through policies that have been implemented purely at the discretion of the executive branch and absent the clearly stated intent of the Congress,” he said in a release.
But Webb’s opposition to major climate initiatives wasn’t limited to executive action. In 2008, Democrats (and a few Republicans) in Congress tried to pass a cap-and-trade bill that was intended to slow global warming by putting a price on carbon emissions. The bill would have likely been vetoed by then-President George W. Bush, but it never got that far. Webb was part of a cohort of Senate Democrats who blocked the measure. “We need to be able to address a national energy strategy and then try to work on environmental efficiencies as part of that plan,” Webb told Politico at the time. “We can’t just start with things like emission standards at a time when we’re at a crisis with the entire national energy policy.”
When cap and trade came up again in 2009—this time with Barack Obama in the Oval Office—Webb again played a major role in preventing the bill from passing the Senate. “It’s an enormously complex thing to implement,” Webb said of the 2009 bill. “There are a lot of people in the middle between the ‘cap’ and the ‘trade’ that are going to make a lot of money.” Webb also voted to prevent Senate Democrats from using budget reconciliation procedures to pass a cap and trade bill with simple majority, essentially dooming any hope for serious climate legislation during the first years of Obama’s presidency.
That same year, Obama attended a United Nations summit in Copenhagen in a failed bid to hammer out an international climate accord. Obama sought a limited, nonbinding agreement in which the US and other countries would pledge to reduce their CO2 output. Webb wasn’t having it. Before Obama went abroad, Webb sent the president a letter asserting that he lacked the “unilateral power” to make such a deal.
Coal wasn’t the only polluting industry that found an ally in Webb. After the BP oil spill in 2010, the Obama administration put a hold on new offshore oil drilling, which provoked Webb. “In placing such a broad moratorium on offshore drilling, the Obama Administration has over-reacted to the circumstances surrounding the Deepwater Horizon disaster,” Webb said in a press release. At other times, Webb championed drilling projects off Virginia’s coasts and voted regularly for bills that would expand the territory in which oil companies could plant rigs offshore. “Unbelievable,” the Sierra Club once remarked of Webb’s support for offshore drilling. In 2012, Webb was one of just four Democrats in the Senate who voted to keep tax loopholes for oil companies.
But it’s Webb’s support for coal that most concerns environmentalists. “Jim Webb is an apologist for the coal industry,” says Brad Johnson, a climate activist who runs the website Hill Heat. “Unfortunately he doesn’t seem to realize that greenhouse pollution is the greatest threat we face to economic justice in this nation.”