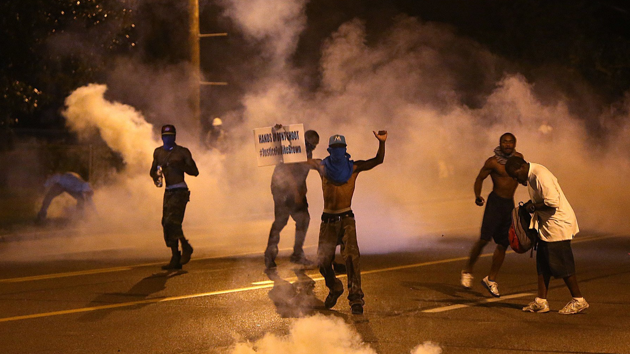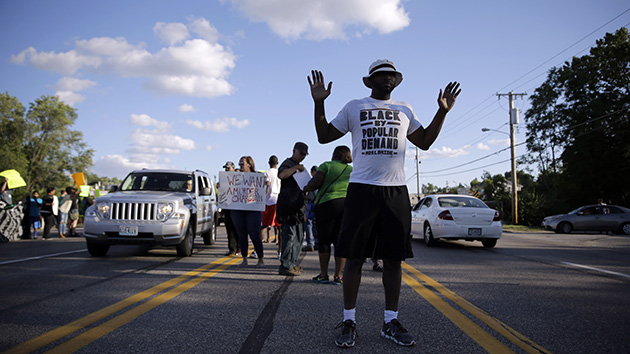
Jeff Roberson/AP
The killing of Michael Brown by police in Ferguson, Missouri, was no anomaly: As we reported yesterday, Brown is one of at least four unarmed black men who died at the hands of police in the last month alone. There are many more cases from years past. As Jeffrey Mittman, executive director of the American Civil Liberties Union’s Missouri chapter put it in a statement of condolence to Brown’s family, “Unarmed African-American men are shot and killed by police at an alarming rate. This pattern must stop.”
But quantifying that pattern is difficult. Federal databases that track police use of force or arrest-related deaths paint only a partial picture. Police department data is scattered and fragmented. No agency appears to track the number of police shootings or killings of unarmed victims in a systematic, comprehensive way.
Here’s some of what we do know:
Previous attempts to analyze racial bias in police shootings have arrived at similar conclusions. In 2007, ColorLines and the Chicago Reporter investigated fatal police shootings in 10 major cities, and found that there were a disproportionately high number of African Americans among police shooting victims in every one, particularly in New York, San Diego, and Las Vegas.
“We need not look for individual racists to say that we have a culture of policing that is really rubbing salt into longstanding racial wounds,” NAACP president Cornell Williams Brooks told Mother Jones. It’s a culture in which people suspected of minor crimes are met with “overwhelmingly major, often lethal, use of force,” he says.
In Oakland, California, the NAACP reported that out of 45 officer-involved shootings in the city between 2004 and 2008, 37 of those shot were black. None were white. One-third of the shootings resulted in fatalities. Although weapons were not found in 40 percent of cases, the NAACP found, no officers were charged. (These numbers don’t include 22-year-old Oscar Grant, who was shot and killed by a transit authority officer at the Fruitvale BART station on New Year’s Day of 2009.)
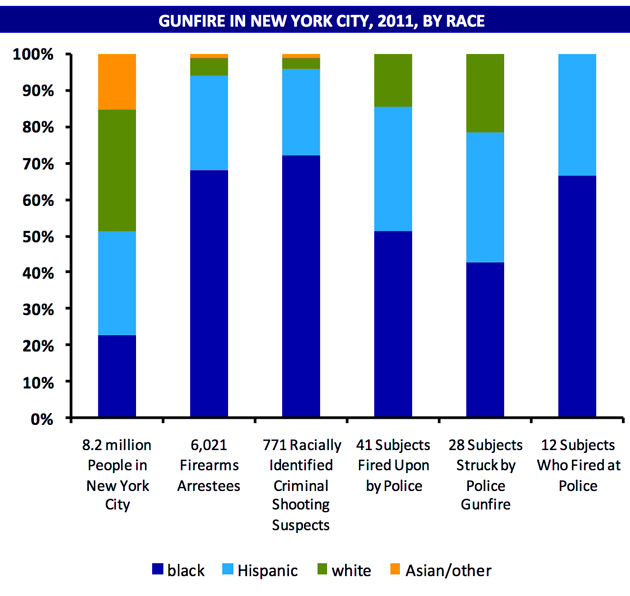
The New York City Police Department has reported similar trends in its firearms discharge report, which shows that more black people have been shot by NYPD officers between 2000 and 2011 than have Hispanics or whites.
When you look at the racial breakdown of New Yorkers, black people are disproportionately represented among those targeted as criminal shooting suspects, firearms arrestees, and those fired upon or struck by police gunfire.
Often, the police officers do not get convicted or sentenced. Delores Jones-Brown, a law professor and director of the Center on Race, Crime, and Statistics at the John Jay College of Criminal Justice in New York City, has identified dozens of black men and women who have died at the hands of police going back as far as 1994. She notes that while these incidents happen regularly, it often takes a high-profile case, such as Brown’s, to bring other recent incidents to national attention.
“Unfortunately, the patterns that we’ve been seeing recently are consistent: The police don’t show as much care when they are handling incidents that involve young black men and women, and so they do shoot and kill,” says Jones-Brown, a former assistant prosecutor in Monmouth County, New Jersey. “And then for whatever reason, juries and prosecutor’s offices are much less likely to indict or convict.”
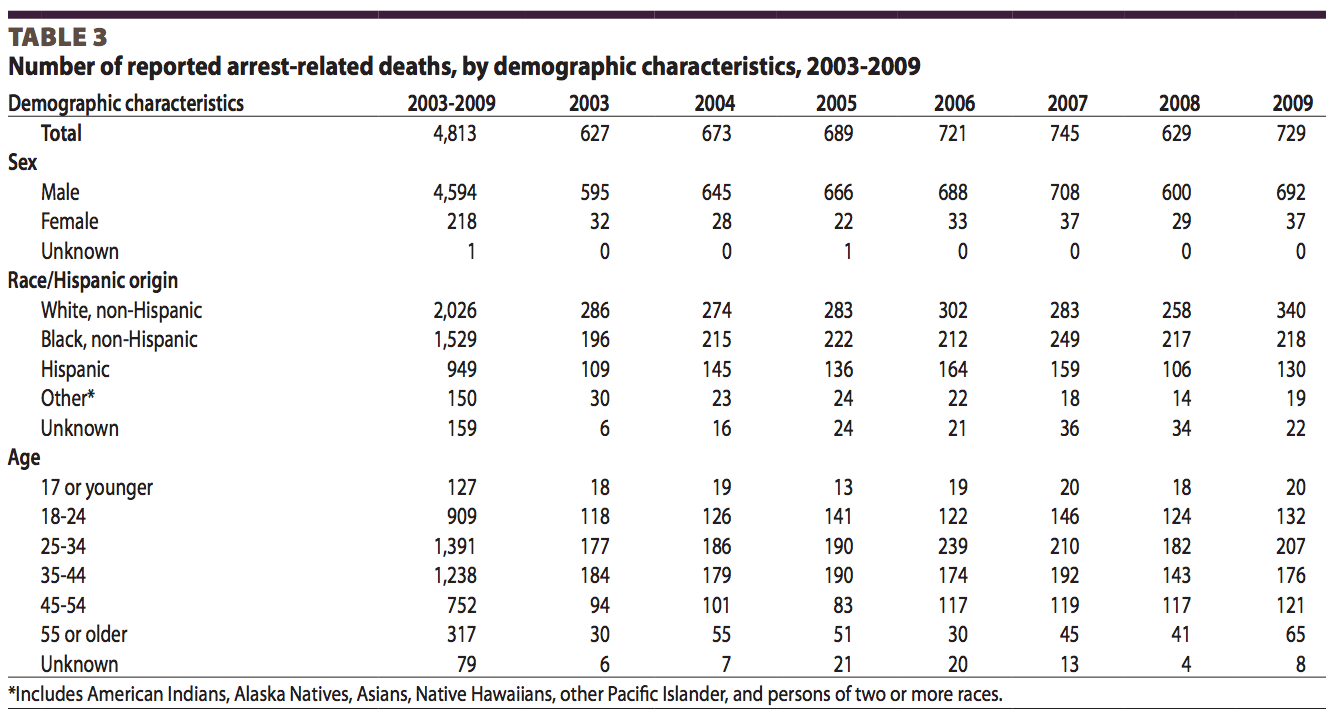
Between 2003 and 2009, the DOJ reported that 4,813 people died while in the process of arrest or in the custody of law enforcement. These include people who died before an officer physically placed him or her under custody or arrest. This data, known as arrest-related deaths, doesn’t reveal a significant discrepancy between whites, blacks, or hispanics. It also doesn’t specify how many victims were unarmed. According to the FBI, which has tracked justifiable homicides up to 2012, 410 felons died at the hands of a law enforcement officer in the line of duty.*
But black people are more likely than whites or Hispanics to experience a police officer’s threat or use of force, according to the Department of Justice’s Police Public Contact Survey in 2008, the latest year for which data is available. Of those who felt that police had used or threatened them with force that year, about 74 percent felt those actions were excessive. In another DOJ survey of police behavior during traffic and street stops in 2011, blacks and Hispanics were less likely than whites to believe that the reason for the stop was legitimate.
The Justice Department has investigated possible systemic abuse of power by police in at least 16 cities.
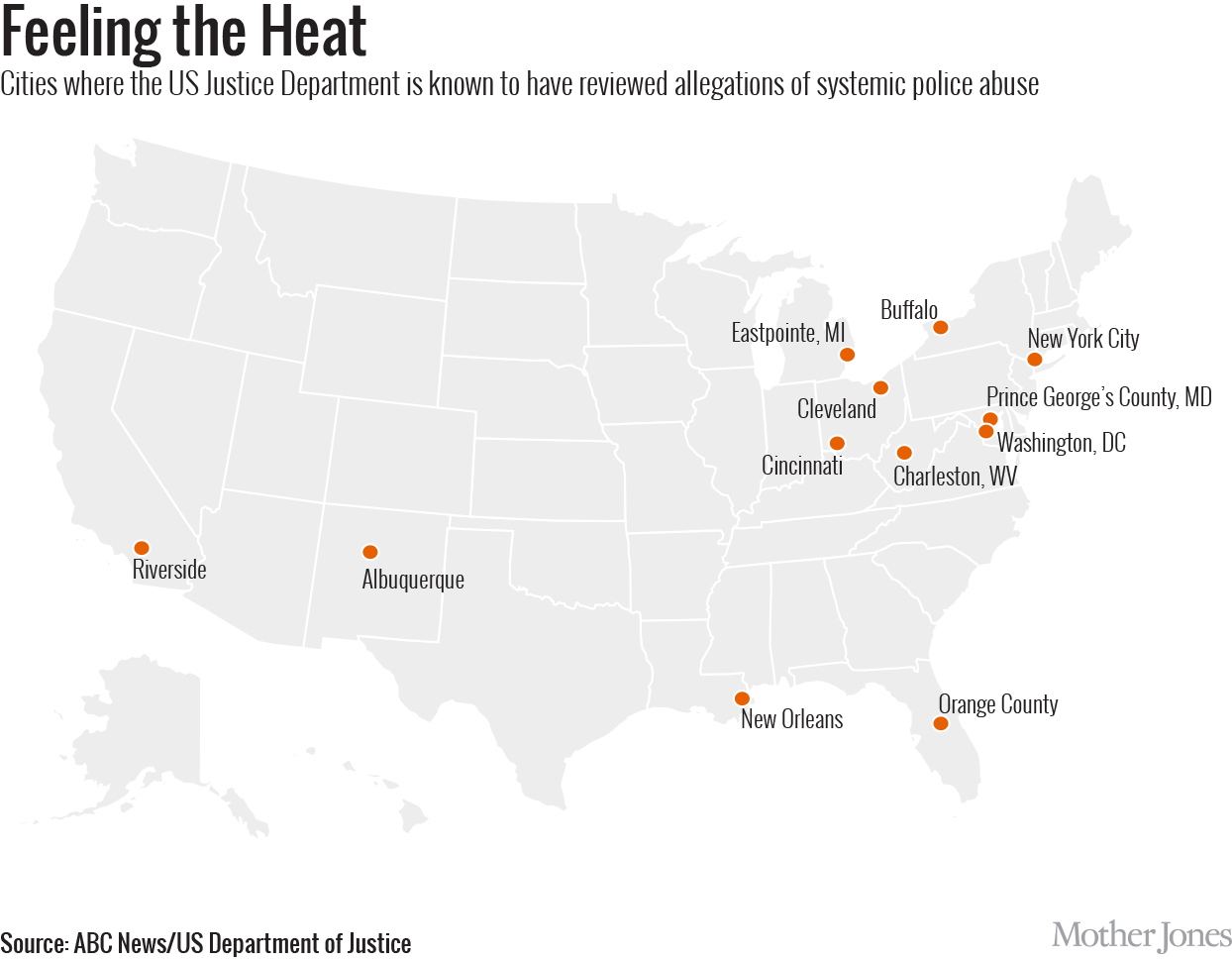
Police shootings of unarmed black people aren’t limited to poor or predominantly black communities. Jones-Brown points to examples where police officers have shot unarmed black men and women in Hollywood, Riverside (California), and Prince Georges County—a Maryland suburb known as the most affluent US county with an African-American majority. “Part of the problem is that black people realize that you don’t have to be poor, you don’t have to be in your own community…and this can happen to you,” she says. These killings occur against black people of varying socioeconomic backgrounds: “Actors, professional football players, college students, high school grads. They happen to black cops, too.”
Yet, the lack of comprehensive data means that we can’t know if there’s been an upsurge in such cases, says Samuel Walker, a criminal justice scholar at the University of Nebraska in Omaha and author of The Color of Justice: Race, Ethnicity, and Crime in America. “It’s impossible to make any definitive statement on whether there were more incidents in the last 5 to 10 years than in the past,” he says. “We just don’t have that kind of data.” But what is certain, Walker says, is that the fatal shooting in Ferguson “was just the tip of the iceberg.”
UPDATE (8/15/14): USA Today reported that on average there were 96 cases of a white police officer killing a black person each year between 2006 and 2012, based on justifiable homicides reported to the FBI by local police. As I reported above, the FBI’s justifiable homicides database paints only a partial picture—accounting for cases in which an officer killed a felon. It does not necessarily include cases involving victims like Michael Brown, Eric Garner, and others who were unarmed when confronted by police. The data in this post has been updated with 2012 numbers, and the map has been updated to reflect that certain cases have been closed.