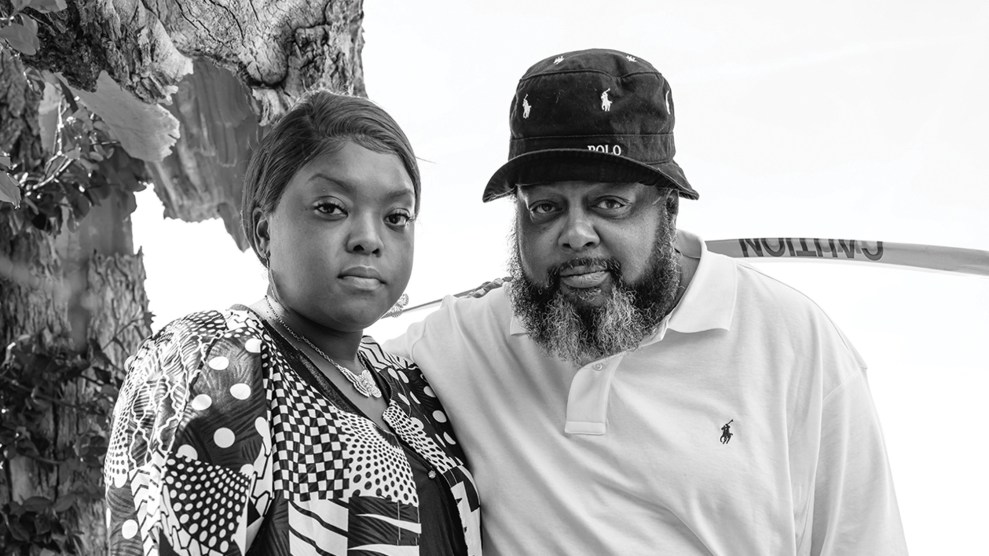
Children sleep under mylar blankets in a makeshift Customs and Border Patrol facility.Ross D. Franklin/AP
In early 2013, three undocumented immigrants sued US Customs and Border Protection for abuse they suffered while spending days in custody. The three women claimed that CBP agents refused to give them soap or toothbrushes; sometimes, agents refused to feed them more than once a day. But the women’s biggest grievance was the unrelenting cold. “Her lips eventually chapped and split,” read one woman’s lawsuit. “The lips and fingers of her two sisters and her sister’s child also turned blue. Because of the cold, she and her sisters and her sister’s child would huddle together on the floor for warmth…There were no mattresses or blankets.”
If you’ve been following the immigration crisis at the Mexican border, you’ve probably heard about these freezing temperatures that migrants endure at border detention facilities. Migrants—especially unaccompanied kids—allege suffering a lot of harm at the hands of CBP agents: sexual assault, beatings, a lack of basic toiletries. But few forms of abuse are more pervasive than the hielera—the Spanish word for “icebox” that detainees and guards alike use to describe CBP’s frigid holding cells.
But why are CBP facilities so freezing?
The answer is elusive. That’s partly because CBP refuses to acknowledge that its detention facilities are consistently cold. Rather, the agency says that cells are kept at about 70 degrees, and it denies that its agents use the term “hielera.”
“We have heard those reports before, and you have to understand, when these folks come in from the desert, they’re hot,” a spokesman with CBP’s Rio Grande Valley sector told me. “They’re sweating…We’re not going to adjust the temperature for a each new group. It would work the system too hard.” He added that keeping the facility at 70 degrees helps control the spread of bacteria.
I replied that many detainees who complain of ice-cold temperatures have not come in from the desert—instead, they have been at a CBP facility for days. “We got that,” the spokesman says. “Sometimes, cells aren’t filled to capacity…and those people may say they’re a little cool.”
In informal talks, immigrant rights advocates say they have heard a different explanation. CBP officials will plead—truthfully—that their facilities were never designed to house migrants for more than a half day or so. And the cold is ideal for CBP agents who spend the day tramping along the border.
“You have agents that are wearing their boots, gear, and bulletproof vests and running around in the desert,” says Jennifer Podkul of the Women’s Refugee Commission. “A comfortable temperature for them is different for a person who’s been in the desert for several days, is wearing a tank top, and is very, very sweaty—and then sits there for two or three days…You wouldn’t believe the hours I’ve spent with CBP talking about the correct temperature.”
Migrants themselves have yet another theory: The cold is part punishment, part deterrent. A Fronteras Desk reporter spoke with an 18-year-old migrant who was detained by CBP along with his younger brother. When the boys complained of the cold, the young man recalls the guard sneering that “maybe we would think about it two times before trying to cross again.”
The specter of the hielera is so strong that even in the heat of summer, immigrants who previously have been detained report that they don’t leave home without a sweater—just in case they are picked up.
“The temperature makes a huge difference to their treatment,” Podkul says. “I’ve talked to children who took the toilet paper they got and laid it on the floor and laid down on that, because it’s one barrier between them and the cement floor.” In 2011, an advocacy group called No More Deaths took an anonymous survey of almost 13,000 former CBP detainees and found that 3,000 respondents had weathered extreme cold.
Like the three anonymous women who sued CBP last year, more and more former detainees are taking their claims to court. In June, Alba Quiñones Flores sued the agency after agents failed to treat her broken ankle and threw away her diabetes medication. CBP guards, she claims, made Quiñones and her cellmates beg for more toilet paper when they ran out. All of this happened, she says, in a holding facility kept freezing cold. Her description may sound familiar: “The cell was so cold,” her lawsuit says, “that Ms. Quiñones Flores’ fingers turned blue, and her lips split.”