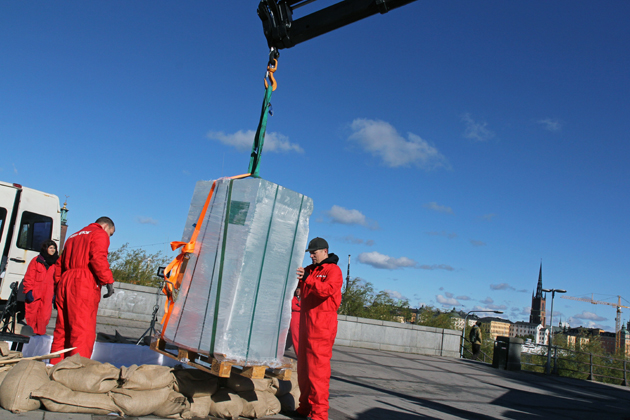
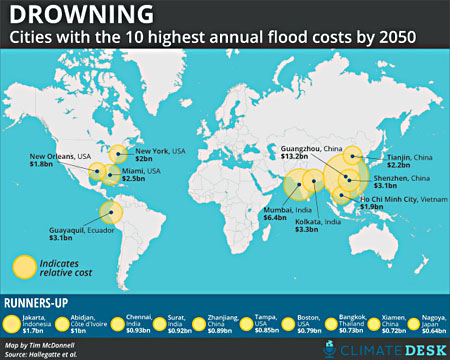
Activists erect a tribute to melting ice outside the IPCC's meeting hall in Stockholm.Tim McDonnell/Climate Desk
Today, on a walkway above Stockholm’s Riddarfjärden bay, four activists in red jumpsuits wrestled with three 2,400-pound chunks of ice. The ice, which will melt onto the sidewalk over the next two days, is meant as a reminder of melting glaciers above the Arctic Circle some 700 miles north of here—although this particular ice was hand-delivered by the same company that maintains Sweden’s famous ice hotel. A few steps away, dozens of top climate scientists from across the globe were sealed in a conference room inside an imposing brick compound that was once one of the city’s largest breweries. They’ve come to hash out last-minute details of the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s Fifth Assessment Report, the last day of a week of tweaks and edits to cap off over five years of work.
“We want to show that the climate change is real,” one of the activists, Valentina Restrepo, said. She’s not likely to face much resistance to that argument from the women and men behind the report: A leaked draft stated that global warming is “extremely likely” (or 95 percent certain) to be caused by human activities. When the report is officially released tomorrow morning, it will be the IPCC’s first global assessment of the state of climate science since 2007, and it’s expected to include updates on everything from how long carbon dioxide hangs out in the atmosphere, to the dangers posed by sea level rise, to the alleged “slowdown” in warming many climate skeptics have trumpeted in recent weeks.

But one question we’ll be asking scientists tomorrow goes beyond the science itself: Is a report like this really necessary? A criticism voiced by many scientists, both within and outside of the IPCC, is that while early iterations of the report were essential tools for alerting policymakers to the dangers of climate change, this fifth report is unlikely to differ significantly from the last report six years ago (which won a Nobel Prize for laying “the foundation” for climate solutions), calling into question the value of dedicating time and resources to re-producing it in its current format.
“If it were up to me, there would not be an AR6 (Sixth Assessment Report),” atmospheric scientist Andrew Dessler told our friends at Climate Central.
There is no original science conducted for these reports; instead, scientists meticulously aggregate, review, and summarize existing literature. While that sounds like a worthwhile endeavor in theory, the amount of time required means that some science (like, as my colleague Chris Mooney reported, on the effects of warming on hurricanes) might be already obsolete by the time it comes out.
Of course, the policymakers who rely on the IPCC to inform their practical approaches to climate change aren’t suggesting that the group disband, but rather break the massive report into more manageable and regularly-issued chunks, according to a survey of participating countries the IPCC conducted earlier this year. This way, the government bureaus that deal with, say, ocean issues, wouldn’t have to sift through a stack of papers on volcanoes to find what’s relevant for them. A new format is one thing that’ll be on the table when members of the group re-convene in Batumi, Georgia, next month.
No matter what form the report takes in the future, its top-line findings tomorrow will form the backbone of climate talking points for at least the next five years, and in Stockholm the coffee is flowing as scientists gear up for a long night of finishing touches (into the “early a.m.,” one wrote to us). Climate Desk will be on the scene all day tomorrow, with live updates from IPCC scientists and other analysis, so stay tuned.