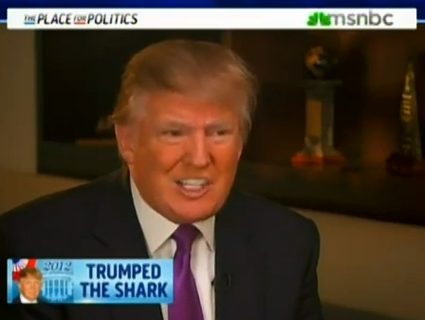
Wastewater left over from fracking wells eventually ends up deep underground, where it can cause earthquakes. <a href=http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Horizontal_Drilling_Rig.jpg>Wikipedia</a>
In November 2011, a destructive 5.7-magnitude earthquake rocked the grasslands outside the small town of Prague, Oklahoma. The shaking leveled 14 homes, shut down schools for repairs, and was felt across 17 states. It also troubled seismologists, who’d never expected an event so large to hit an area that was supposed to be seismically safe.
According to the results of a new study published online yesterday in the journal Geology, the temblor was potentially linked to the underground injection of wastewater from local oil operations. In fact, the fault that triggered the event ruptured just about 200 meters from active injection wells. Changes in water volumes deep underground may have reduced the stress on the rock, allowing the fault to slip.
The underground disposal of wastewater has skyrocketed due to the recent uptick in hydrofracking operations across the country. Other studies have linked wastewater injection wells to earthquakes in otherwise seismically quiet areas of Arkansas, Texas, Ohio, and Colorado. The Oklahoma quake, however, was the most powerful.
For the current issue of Mother Jones, contributing writer Michael Behar followed Katie Keranen, the lead author of the Geology study, into the fields of the Sooner State for an elegant look at the science behind the link between earthquakes and the oil and fracking industries. Behar also interviewed seismologists and government officials who are increasingly concerned that loose regulations on wastewater injection could cause the next big one in a region unprepared for seismic activity. And he details the shadowy ties between industry and science that may complicate meaningful regulatory change.
Catch the full story here.