Matt Yglesias calls this a “wild” result. It’s from a new NBER paper by a trio of researchers:
Medical and public health innovations in the 1940s quickly resulted in significant health improvements around the world. Countries with initially higher mortality from infectious diseases experienced greater increases in life expectancy, population, and — over the following 40 years — social conflict. This result is robust across alternative measures of conflict and is not driven by differential trends between countries with varying baseline characteristics. At least during this time period, a faster increase in population made social conflict more likely, probably because it increased competition for scarce resources in low income countries.
Initially, I was intrigued because this seemed like a distinctly un-wild result. Fast population growth as a cause of war seems like conventional wisdom, not something new. But I was curious, so I took a look at the paper. Stripped to its core, the authors present an equation that looks like this:
Conflict = 0.617 * log(Population)
They say that this “implies that the average change (0.676) in log population from 1940 to 1980 leads approximately to 4.17 more years in conflict during the 1980s relative to the 1940s.” In ordinary language, it means that a doubling of population leads to about 4.3 more years of conflict per decade. Here’s their chart:
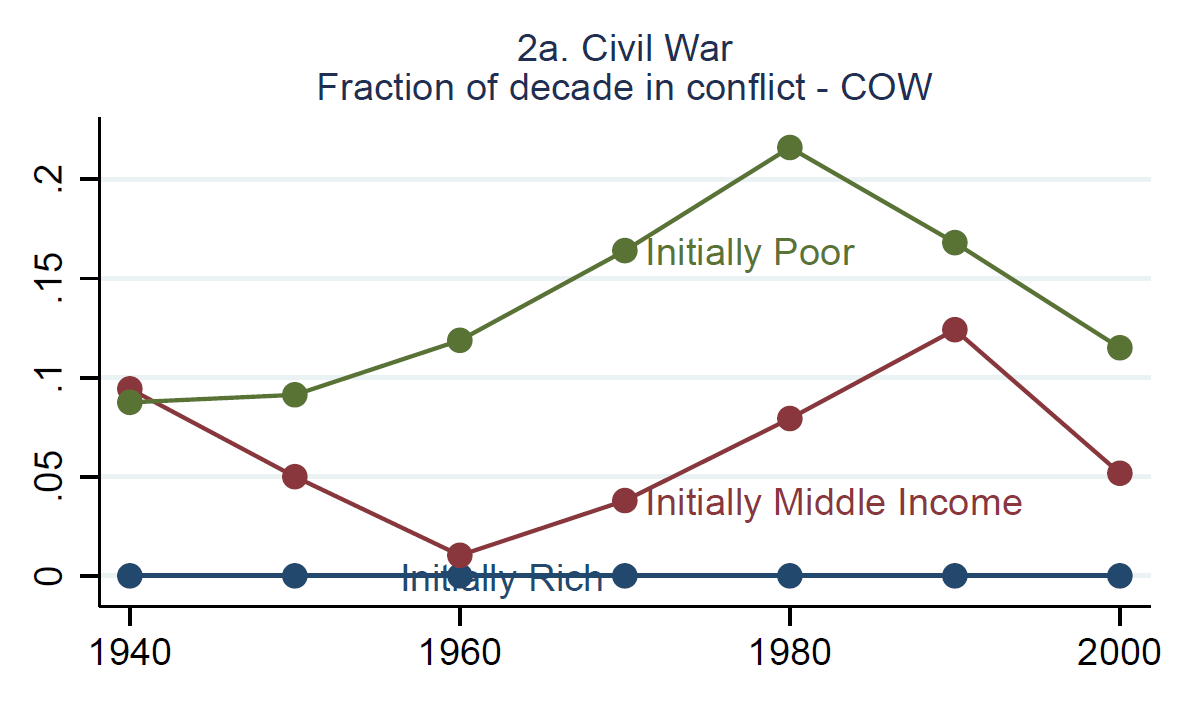
I have some issues here. First, the authors say that a “faster increase” in population makes social conflict more likely—which makes sense—but their regression equation says only that bigger countries have more conflict, not faster growing countries. Second, the basic correlation here is that from 1940-80, both population and conflict grew. They believe that population growth spurred by health improvements caused conflict to increase, but the universe of possible explanations for this is almost limitless.1 Third, the correlation suddenly breaks down after 1980.
The authors suggest that “increasing population without a corresponding increase in resources and technology, raised the likelihood of civil war — presumably because there was an more intense competition for scarce resources.” Again, this makes sense, but in fact there was an increase in resources. World population roughly doubled from 1940-80, but thanks to the Green Revolution, so did the production of cereal grains:
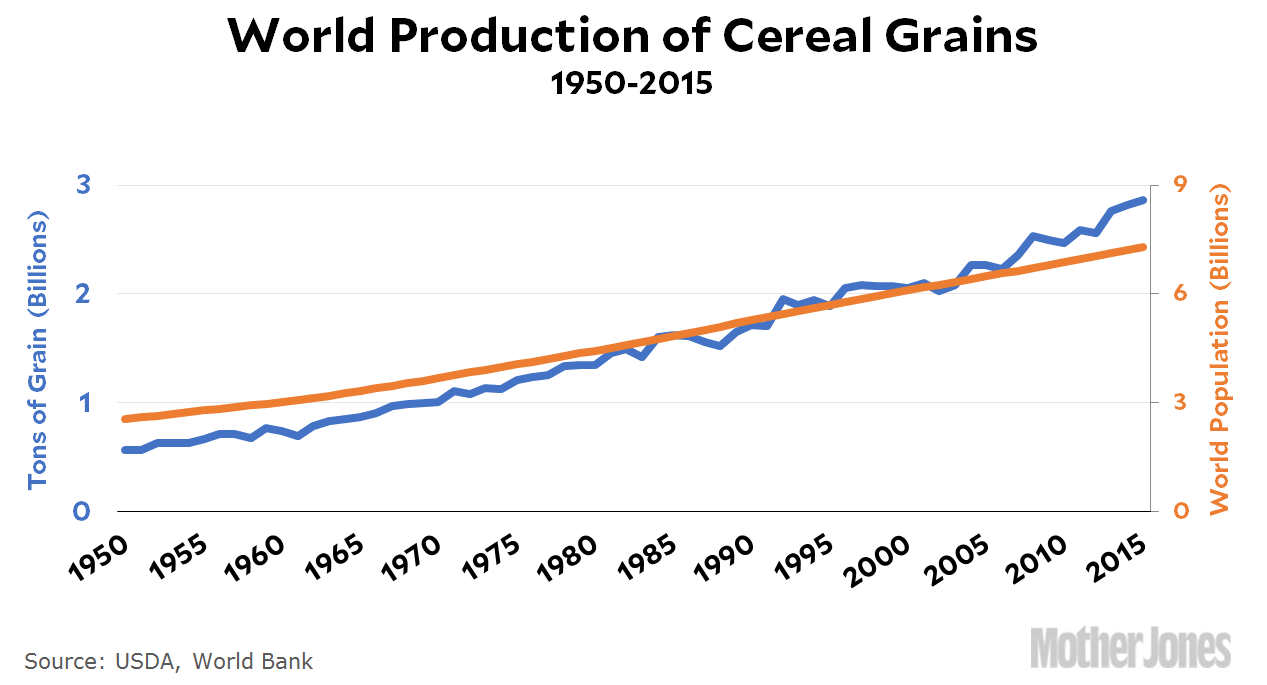
Food production increased faster than population growth from 1940-80, but conflict increased anyway. It continued to increase faster than population growth from 1980-2015, and conflict decreased. The authors suggest there’s something special about the earlier period, but don’t really provide any idea of what that might be. If I had to guess, I’d suggest the culprit is decolonization following World War II. That would explain both the increase from 1940-80 and the decrease after that. But this is just a guess.
1Before anyone asks: Given the timeframes involved here, lead is not likely to be a major factor. But it might have added a tailwind.