I post here periodically about declining European inflation and rising European unemployment, and today Paul Krugman draws our attention to an IMF blog post about the threat of actual deflation in Europe. The bottom line is that there’s no actual deflation—yet—in most of Europe, but there is in three countries, and there’s persistently low inflation across the continent:
- Although inflation—headline and core—has fallen and stayed well below the ECB’s 2% price stability mandate, so far there is no sign of classic deflation, i.e., of widespread, self-feeding, price declines.
- But even ultra low inflation—let us call it “lowflation”—can be problematic for the euro area as a whole and for financially stressed countries, where it implies higher real debt stocks and real interest rates,
 less relative price adjustment, and greater unemployment.
less relative price adjustment, and greater unemployment. - Along with Japan’s experience, which saw deflation worm itself into the system, this argues for a more pre-emptive approach by the ECB.
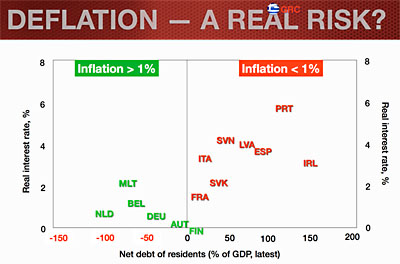
The chart on the right illustrates one of the big problems with “lowflation,” even if it doesn’t turn into outright deflation: the countries with the lowest inflation are also the ones with the highest debt levels and the biggest growth problems. They need to reduce wages relative to other countries, but with low inflation that’s very hard to do. It requires actual pay cuts, something that’s historically difficult, rather than simply freezing wages and allowing them to erode via inflation. As a result, it’s hard for their economies to recover, and that in turn makes it all but impossible to fix their debt problem. It’s a vicious spiral.
Krugman warns that without more aggressive policy from the European Central Bank, the EU risks following Japan into economic stagnation: “When people warn about Europe’s potential Japanification, they’re way behind the curve. Europe is already experiencing all the woes one associates with deflation, even though it’s only low inflation so far; and the human and social costs are, of course, far worse than Japan ever experienced.”
In related news, I’ll also draw your attention to China’s latest woes: “China’s leaders kept the growth target for their giant economy unchanged but signaled that they are more concerned than ever about reaching it, giving themselves the option of letting credit flow freely to keep from falling short.” In the long run, China’s slowdown was inevitable as wages rose and demographic realities intruded. But it’s bad news in the short term. With the economy still flat in the US; European recovery threatened by debt and deflation; Chinese growth getting harder to come by; and the developing world seemingly running out of steam—with all that happening at once, there aren’t very many bright spots in the global economic picture. At best, it looks like we have fairly gray times ahead of us. At worst—well, it might be worse.