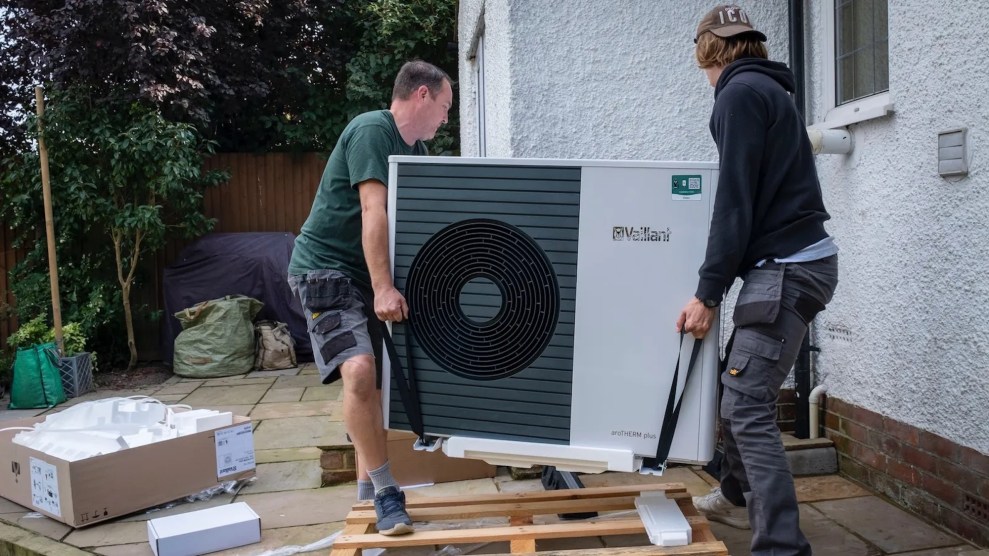
Getting ready to install a new heat pump.Andrew Aitchison/Getty Images/Grist
This story was originally published by Grist and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
Making homes more efficient and more electric is critical to combating climate change. But the undertaking can be expensive and beyond the financial reach of many families.
Help, however, is on the way.
Residential energy use accounts for one-fifth of climate-warming greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. President Biden’s landmark climate bill, the Inflation Reduction Act, takes aim at this issue by allocating $8.8 billion to home energy efficiency rebates primarily for at low- and moderate-income households.
“For the federal government, this is the largest investment in history,” said Mark Kresowik, senior policy director at the nonprofit American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy. “These rebates have the potential to provide tremendous support, particularly for low-income households, in terms of reducing pollution, reducing energy costs, and making homes more comfortable.”
States will administer the rebate programs under guidance the Department of Energy released in late July. The money could become available to consumers as early as the end of this year, though the bulk is expected throughout 2024. In some cases, the incentives could cover the entire cost of a project.
Incentives will fall into two buckets, with about half designated for home electrification and the remainder going toward overall reductions in energy use. The funding will be tied to household income.
States must allocate about 40 percent of the electrification money they receive to low-income single-family households and another 10 percent toward low-income multifamily buildings. The rest of the electrification rebates must go to moderate-income households. These are minimums, said Kresowik, noting that states can, and some likely will, make even more of the rebates need-based.
Income limits are location dependent and set by the Department of Housing and Urban Development. Low income is defined as 80 percent of area’s median household income, while moderate income is up to 150 percent. What that means can vary widely. In San Francisco, for instance, the low income threshold for a family of four is $148,650, while in Bullock County, Alabama it’s $52,150.
The rebates also are larger for low-income households. On the electrification front, the guidelines call for up to $8,000 for heat pumps, $840 for induction stoves, and $4,000 to upgrade an electric panel, among other incentives. That said, no single address can receive more than $14,000 over the life of the program. The discounts are largely designed to be available when the items are purchased, which avoids having to paying out of pocket and waiting for a check from the government.
“These are advanced technologies. Therefore they often cost more, but they save more energy and help save the climate,” said Kara Saul-Rinaldi, president and CEO of the AnnDyl Policy Group, an energy and environment strategy firm. “If we want our low-income communities to invest in something that’s going to benefit everyone, like the climate, we need to provide them with additional resources.”
For the energy-reduction incentives, the type of technology used doesn’t matter as long as households lower their overall energy use. Homeowners could do this by installing more insulation, sealing windows, or upgrading to more efficient heating and cooling systems, among other options. The rebate amounts are a bit more complex to calculate but are based on either modeled or actual energy savings, and increase if you save more energy or are low income.
Kresowik says efficiency retrofits can cost $25,000 to $30,000 or more. For many people, the Inflation Reduction Act could help put such projects within reach for the first time. While a homeowner cannot claim both an electrification and efficiency rebate for the same improvement, the incentives can be added to other federal weatherization and tax credit initiatives and any offers from utility companies.
But the latest rebates will be available only after states have set up their respective programs. For that reason, “the families who most need that help will be better served to wait if they can,” said Sage Briscoe, director of federal policy for the electrification nonprofit Rewiring America. Of course, that may not be feasible if, say, an appliance breaks, but doing so could potentially net a low-income household thousands of dollars in savings.
“The key is to start planning,” Kresowik said of the coming rebates. Talking to a contractor now, he said, can position households to take advantage of the programs as soon as they start accepting claims.
The rebates, though, may not be available everywhere. Florida, Iowa, Kentucky, and South Dakota have so far declined to apply for Inflation Reduction Act funds and could reject the home energy rebates as well. That means a sizable number of Americans may not see a boon from these latest rebates, either because they earn too much money or live in a state that refuses to participate in IRA programs.
Federal tax credits, however, are available now to help anyone pursuing projects such as installing solar panels or heat pump water heaters. The credits reset annually, but because they offset tax liabilities, the ability to fully utilize them often depends on a filer’s tax burden.
“There are those among us who are privileged enough that they probably can go ahead and start making those investments now,” said Briscoe. Rewiring America is in the process of launching tools to help people plan for, claim, and receive incentives, which can be complicated. But experts say that even this influx in funding won’t ultimately be enough to meet the need nationally.
“This is just a drop in the bucket,” said Saul-Rinaldi. Kresowik notes that there are 26 million low-income households that still use fossil fuels for heating. At $30,000 each, electrifying those homes alone would cost $780 billion.
Saul-Rinaldi also sees a risk that the current program is limited by quirks in the guidance from the Department of Energy that may keep some contractors from participating, such as mandating in-person energy audits, even when utility data would suffice. But, she says, there is still time to smooth out those issues, and she hopes that the programs are “so successful that there is a wide demand across the country for additional funds so that we can continue to upgrade and electrify America’s homes.”
Ideally, Briscoe wants to see high-efficiency appliances and design become the norm, and she thinks incentives can help push the market in that direction. Previous federal rebate efforts, such as a Great Recession stimulus bill included $300 million in appliance efficiency funding, didn’t quite do that. But Briscoe says this latest attempt through the Inflation Reduction Act is not only orders of magnitude more ambitious but also more holistic and works in concert with other programs—such as installer training initiatives—to ensure the rebates aren’t operating in a vacuum.
“There’s some real urgency to making sure that we try to get the fossil fuels out of our homes,” said Briscoe. “The climate isn’t going to wait.”