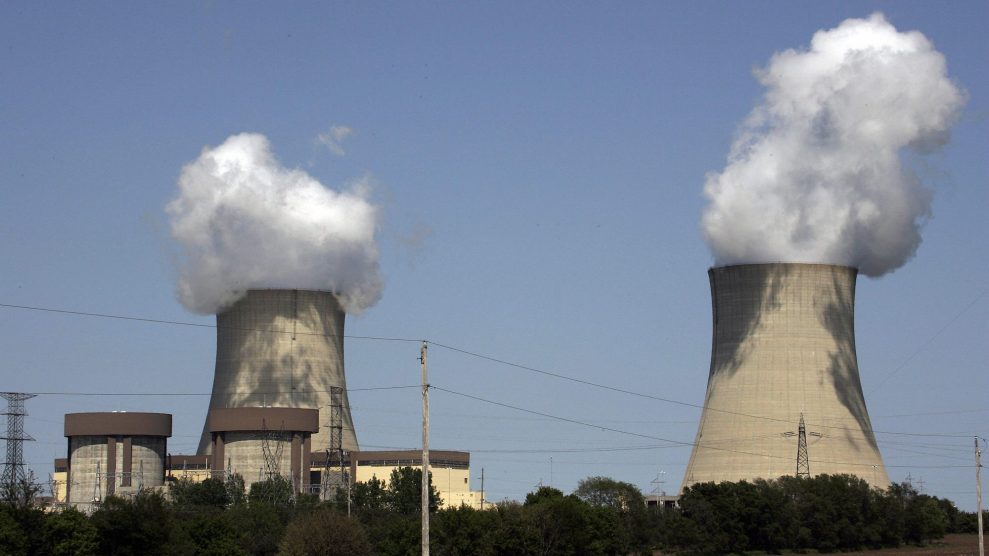
The Exelon Byron Nuclear Generating Stations running at full capacity 14 May, 2007 in Byron, Illinois.
Jeff Haynes / Getty
This story was originally published by the High Country News and appears here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
Nuclear power generates electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other air pollutants. Yet it hasn’t been extensively deployed to fight climate change because of safety fears, the high cost of construction and, perhaps most significantly, the hazardous waste, or spent fuel, reactors produce. Now, as the climate crisis worsens, pro-nuclear groups are speaking out.
One such group, Generation Atomic, argues that nuclear power doesn’t really have a waste problem. All 88,000 tons or so of waste produced by reactors in the US could fit onto a single football field, stacked just 24 feet high, it says, with the waste produced by an individual’s lifetime energy consumption fitting in one soda can. Compare that to the 100 million tons of solid waste—about a 5-mile-high pile on a football field—that US coal-fired power plants kick out each year.
These figures are accurate, but incomplete: They leave out several steps that precede the power generation phase, each of which produces sizable quantities of hazardous and radioactive waste. By omitting these, we risk ignoring the bulk of the nuclear industry’s human and environmental toll.
The following diagram quantifies the waste that is produced, from mining to power generation, from a year of power production—enough for about 2.44 million households—at a plant the size of Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station in Arizona. It would take about 1.7 billion soda cans, or a football field stacked 580 feet high, to contain just one year’s waste.
NUCLEAR WASTE
Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station generates about 31,000 gigawatt-hours of power each year. That requires about 86 tons of uranium oxide, enriched to 3-to-5 percent uranium-235. In order to produce that, you need to:
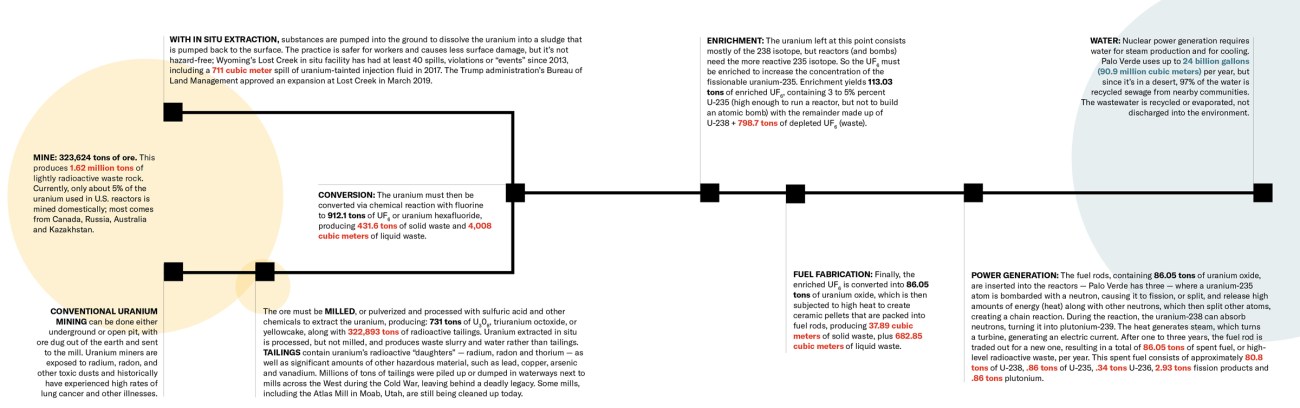
Sources: Waste and Environment Safety Section of the International Atomic Energy Agency; U.S. Energy Information Administration; Generation Atomic; Nuclear Energy Institute; World Nuclear Association; Arizona Public Service; WISE Uranium Project.
Luna Anna Archey / High Country News
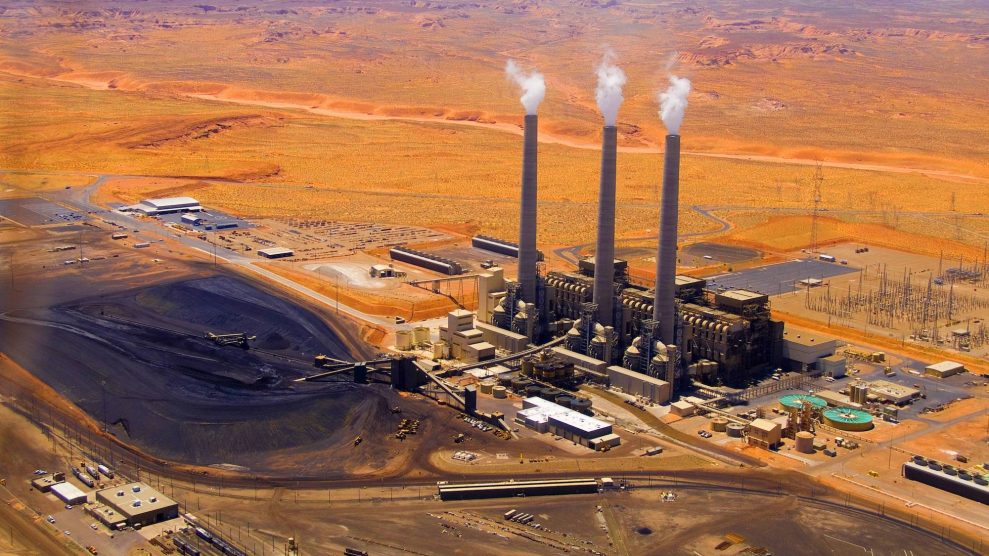
… AND THEN THERE’S COAL
In order for a coal-burning power plant to produce 31,000 gigawatt-hours per year, or the same amount of electricity generated by Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station, you would need to:

Sources: Waste and Environment Safety Section of the International Atomic Energy Agency; U.S. Energy Information Administration; Generation Atomic; Nuclear Energy Institute; World Nuclear Association; Arizona Public Service; WISE Uranium Project.
Luna Anna Archey / High Country News