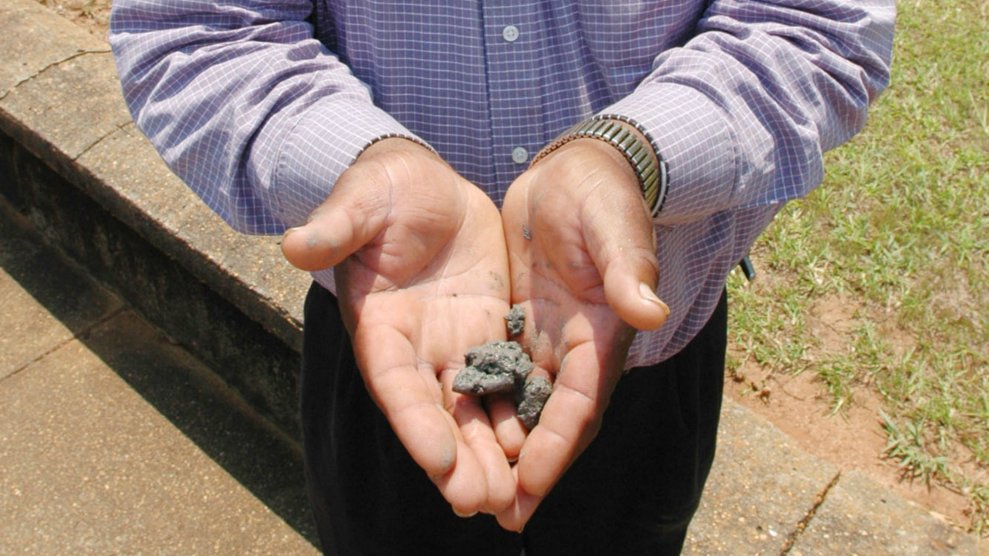
A man holds a lump of coal ashJay Reeves/AP
The residents of Uniontown, a poor, majority-black town in rural Alabama, are used to being ignored by the federal government. For years they have fought against the Arrowhead landfill, a site that they say is negatively impacting the environment and forcing residents to cope with offensive odors, upper respiratory infections, headaches, and vomiting among other symptoms. The Environmental Protection Agency accepted a civil rights complaint from Uniontown in 2013, but earlier this month, the EPA announced that its External Civil Rights Compliance Office was “resolving and closing” the complaint citing “insufficient evidence” to find that the state violated any civil rights.
Have their options run out? “They’re not giving up by any stretch,” says Marianne Engelman Lado, a Yale University professor who helped represent Uniontown residents. Even after receiving the disappointing news from the EPA, residents are not going to back off. “We will continue to pursue every means that we can,” said Ben Eaton, the vice president of Black Belt Citizens Fighting for Health and Justice. “Uniontown is a good place, with good people, even though we have an uphill battle to fight for our environmental civil rights.”
Toxic waste sites, such as landfills and oil refineries, are more likely to be located in communities of color so the pollution from these sites often has a disproportionate effect on marginalized people. This makes environmental justices an integral part of the civil rights movement. Just weeks after the EPA announcement, the US Commission on Civil Rights issued a blistering statement about the EPA’s decision. “Sadly, these dismissals continue the EPA’s disturbing and longstanding track record,” it said. In 2016, the agency released a report that documented the EPA’s dismal failure to enforce civil rights. “We will continue to monitor the EPA’s enforcement of federal civil rights statutes,” the statement said, “and find this is yet another distressing step in the wrong direction for the agency.”
Uniontown is in Alabama’s Black Belt, a region in the central portion of the state that was once dominated by slave owners. The town is majority-black and poor with 48 percent of individuals living below the poverty line. Even before the landfill opened—which was designed to receive waste from over half the country—the people of Uniontown were against it. They formed the Black Belt Citizens Fighting for Health and Justice to stop its construction by suing the Alabama Department of Environmental Management and the Perry County Commission, but a trial judge ruled against them.
Nonetheless, the Arrowhead landfill opened in 2007 and soon after, dust, foul odors, and flies became a part of daily life for the people living nearby. “People talk about how the paint peels from the cars,” Esther Calhoun, the president of the Black Belt Citizens Fighting for Health and Justice, told Grist in 2016. “And there’s dust everywhere, everywhere. There’s buzzards everywhere, too.”
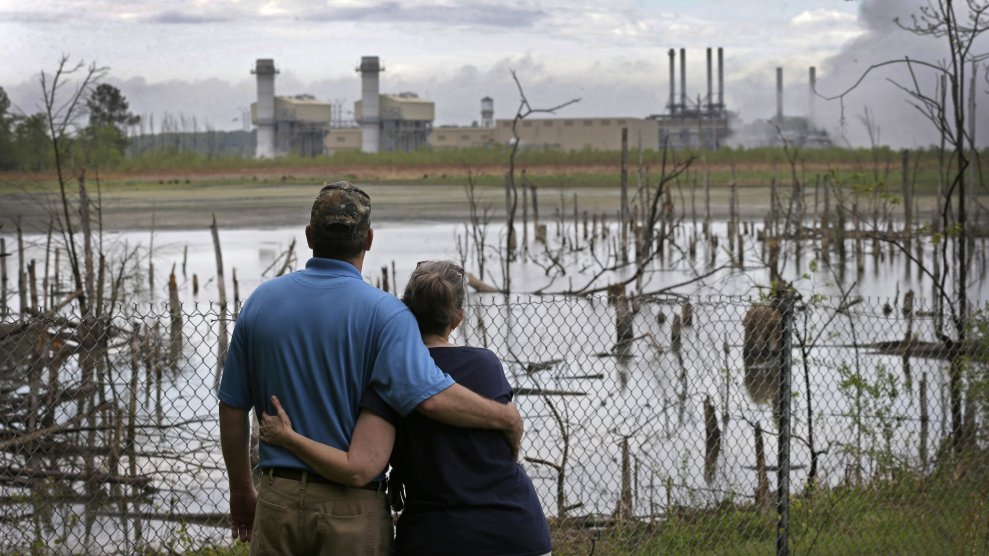
The following year, a disaster hundreds of miles away became Uniontown’s problem. In December 2008, a retaining wall at the Kingston Fossil Plant gave way in the middle of the night and more than 1 billion gallons of coal ash, the toxic byproduct of burning coal, spilled into the Tennessee River and on more than 300 acres of land. Three homes were destroyed and dozens were damaged. Even though no one was killed, the coal ash sludge, which contains hazardous chemicals such as arsenic and mercury, remained and needed to be cleaned up.
In 2009, with the blessing of local leaders and against the wishes of the residents, the Tennessee Valley Authority, the owner of the plant, began shipping its coal ash to the Arrowhead landfill. At the time, Bob Deacy, TVA’s vice president of clean strategies and project development told the New York Times that Arrowhead was chosen because it was accessible by train instead of truck, had the capacity to hold all the coal ash, and local leaders had underbid all the other offers.
Meanwhile, Uniontown residents had mobilized to fight back. In 2012, they filed their first complaint against the Alabama Department of Environmental Management, the agency in charge of issuing permits for the landfill. The complaint alleged that because ADEM permitted the landfill, it was violating Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits recipients of federal funds from taking actions that have disproportionate adverse effects on the basis of race. The complaint described the dire health consequences of living near the landfill, they also said that dust from the coal ash collected on their homes, plants, and cars. The presence of the landfill has decreased property values. After six years, the EPA issued their final decision this month, saying there was insufficient evidence to find any discrimination.
Lawyers working with them suggest that there may still be some legal options. “We are still looking at further legal action,” Claudia Wack, a member of Yale Law’s Environmental Justice Clinic told the Selma Times-Journal. “We are keeping up the good fight.”
Faced with this setback, residents still are trying to make a difference on the local level by continuing to pressure ADEM. Some have decided to run for office to replace the town leadership that they believe got them into this situation in the first place. Ben Eaton, BBCHJ’s vice president, has been inspired to run for county commissioner to add his voice to those of the commissioners who “originally voted to allow the coal ash to come into Uniontown.” In terms of mounting an effective opposition, Engelman Lado said, running for office is “a really important part of their strategy.”
The Black Belt Citizens Fighting for Health and Justice has also continued to organize actions surrounding environmental concerns in their community. The group has scheduled events to attend Uniontown city council meetings to voice their concerns about pollution and other injustices.
Uniontown residents may not have been surprised about the outcome, given the EPA’s history of ignoring civil rights complaints, but they were still disappointed. “When you go Uniontown, you smell that landfill,” Engelman Lado says. “You don’t need a peer reviewed study to tell you it’s affecting peoples’ lives.”