This month, an eerily precise annual migration began in earnest on a tiny Australian island about 500 miles off the coast of Indonesia.
Every year, millions of adult red crabs—first the males, then the females— scamper out from Christmas Island’s central forests, across the island, and finally to beaches that meet the Indian Ocean. Their goal is to stage one giant crab sex party: to mate and spawn.

According to Christmas Island National Park authorities, “the females will spend two weeks brooding their eggs before making their way to the cliffs and beaches to spawn. This should occur about the 18th-19th of December. Before sunrise on these mornings the females will release their eggs into the ocean—timed perfectly for the receding tide.”
Amazing.

Watch them below making their slow, deliberate, hard-wired journey:

Parks Australia says that there are tens of millions of crabs—20 species in total—that live on the island. Their migration occurs between October and December and is triggered by rains characteristic of the island’s tropical wet season.
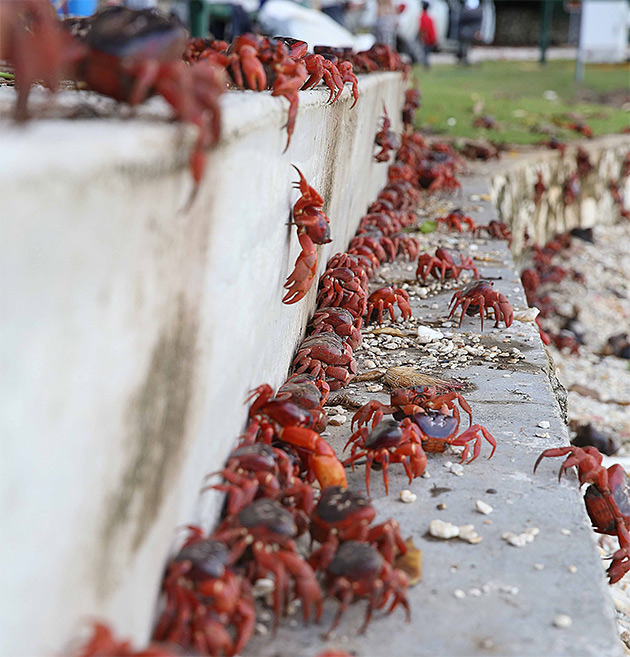



Wildlife rangers have installed up to 7.5 miles of crab fences along the roads, according to Parks Australia—and every year they add up to three miles of additional temporary fencing—to help protect the crabs and their mating rituals. There are already 34 “crab crossings,” which are basically culverts under the roads so the crabs can avoid the cars. Here’s a video explaining just how elaborate the preparations have become:
Behind the scenes of the red crab migration – Christmas Island 2012 from Parks Australia on Vimeo.
But this spectacular beach invasion may be threatened by global warming. Research conducted by Princeton University found that increasingly unpredictable rainfall—potentially a symptom of climate change—could harm the red crustaceans’ chances of a successful journey, and therefore imperil their survival.
The study, published in Global Change Biology, found that if fluctuations in rainfall become more extreme and frequent, the crabs might get scrambled and not even start their migration, which is what happened during an exceptionally dry 1997 season. “We found that the start date of the migration was really dependent on the rainfall they received in the weeks before the migration,” said Allison Shaw, an author of the study, and now an assistant professor at the University of Minnesota. “The issue for the crabs is that they have to migrate if they want to produce. If they can’t make it to the water, they won’t produce offspring.” Disturbances in the migration patterns were linked in particular to strong El Niño years, which tend to make Christmas Island dry, Shaw says.
There’s still a lot of science yet to be done to clear up the connection between El Niño and climate change, but trends are emerging. “The 20th century is significantly, statistically stronger in its El Niño Southern Oscillation activity than this long, baseline average,” Kim Cobb, Associate Professor of Climate Change at the Georgia Institute of Technology, told me last year. That is, El Niño events have gotten worse.
If that’s the case, Christmas Island, home to the crabs, will experience more intense, and therefore drier periods, says Shaw. A lack of rain can delay or entirely cancel the crimson tide of crabs, and the resulting swarms of crab offspring, seen below.