Oil covers the ground after a 2010 well blowout near Cheyenne, Wyoming. The state leads the nation for uninspected wells on federal land. (The inspection status of this particular well is unknown.) AP
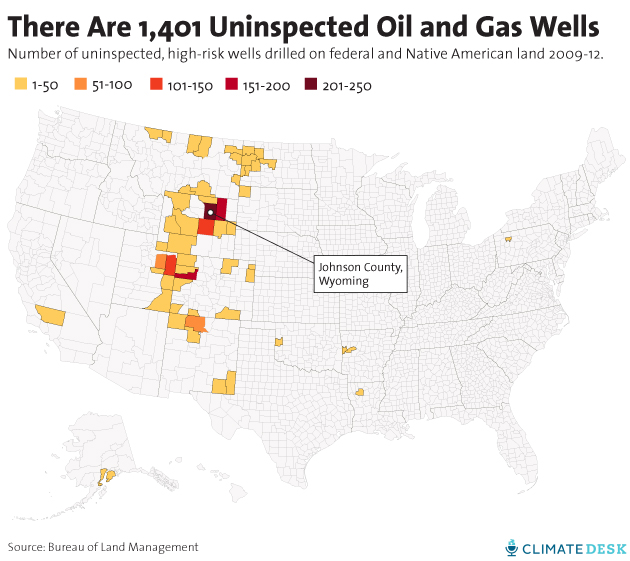
Johnson County, Wyoming, is the kind of remote, quiet Western community where life revolves around cattle—it was the site of an infamous 19th-century armed battle between cowboys and suspected cattle rustlers. The county ranks only 11th statewide for oil production, but it holds the No. 1 ranking nationwide for a more ignominious distinction: It has 249 new, high-risk oil and gas wells that the federal government has failed to inspect for compliance with safety and environmental standards.
Johnson County may have the most uninspected wells, but it’s far from the only place where the problem exists. In fact, of all 3,486 oil and gas wells drilled on federal and Native American land from 2009 to 2012 that were identified by the Bureau of Land Management as high risk for pollution, 40 percent were not inspected at the most important stage of their development, according to records the BLM provided to Climate Desk.
“In a perfect world, we’d love to get to all those wells,” said Steven Wells, chief of the BLM’s Fluid Minerals Division. “Unfortunately we’ve been fighting an uphill battle. We hope that at some point we’ll be able to catch up.”
The map and chart below identify where these wells are located, by county:
In May, the Government Accountability Office estimated that an even larger share of new wells on federal land—57 percent—were not inspected. While the revised 40 percent figure, which was first reported by the Associated Press, is lower, it’s “still not a very good number,” acknowledged BLM spokesperson Bev Winston.
Between 2009 and 2012, the BLM tagged 3,486 new oil and gas wells as “high-priority,” meaning they are deserving of special scrutiny because of their proximity to ecologically sensitive areas like watersheds and forests, or because they tap into geologically volatile formations that increase the likelihood of an explosion or toxic gas leak. The data includes both conventional and unconventional wells and does not indicate how many of the wells were hydraulically fractured, or fracked.
According to the GAO report, the agency’s own rules call for all high-priority wells on federal and Native American land to be inspected during the drilling stage. That’s the only time when key facets of a well’s construction—whether the well casing is properly sealed, or whether a blowout preventer is correctly installed, for example—can be adequately inspected. Once the well is drilled, retroactive inspection becomes difficult or impossible, according to a BLM engineer.
Because the window for drilling inspections at any given well opens and closes so quickly, the BLM is often spread too thin to get to all of them, the engineer said. Some wells receive inspections later on to check the functioning of their machinery, but the drilling stage is the only opportunity to scrutinize a well’s construction.
Wells agreed that BLM field offices are forced to triage their inspection efforts due to a shortage of boots on the ground. The staffing problem has only gotten worse in recent years, he said, as federal budget cuts have coincided with aggressive efforts by the booming energy industry to hire the best engineers away from government jobs.
“We’re scattered, and you can’t be everywhere at once,” Wells said.
Wyoming led the nation with the highest proportion of uninspected wells. Although the state was one of the nation’s top oil producers from 2009 to 2012, 45 percent of its new, high-priority wells drilled during that window were not inspected. Wyoming is the state with the most BLM-managed wells, Wells said, so “just by sheer numbers, they have the most number of wells to miss.”